Water and Wastewater Reuse
Faced with these challenges, there is an urgent need to improve the efficiency of water consumption, and to augment the existing sources of water with more sustainable alternatives. Wastewater reuse has become increasingly important in water resource management for both environmental and economic reasons. In cities and regions of developed countries, where wastewater collection and treatment have been the common practice, wastewater reuse is practiced with proper attention to sanitation, public health and environmental protection.
Wastewater reuse may be applied in agriculture, industry, groundwater recharge, and urban usage, including landscape irrigation and fire protection. Wastewater reuse can be adopted to meet the water demand in different fields and contribute to the conservation of freshwater resources.
Wastewater can be recycled within the same industrial process or for another application such as in agricultural irrigation, with or without treatment to meet specific quality requirements. It can also be used for cascading use, which refers to a practice of using water in sequence for different applications. If the quality is not suitable for direct cascading use, wastewater can be reclaimed with adequate treatment, or used after dilution with clean water or other higher quality wastewater.
Wastewater reuse processes can be categorized into the following three:
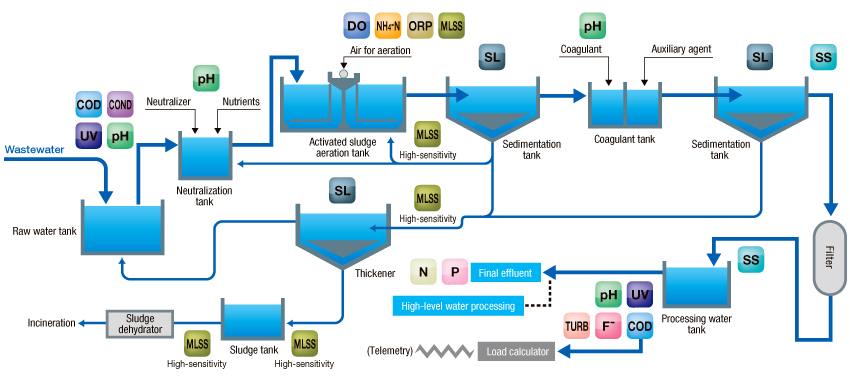
- Physical process: impurities are removed physically by screening, sedimentation, filtration, flotation, absorption or adsorption or both, and centrifugation;
- Chemical process: impurities are removed chemically through coagulation, absorption, oxidation-reduction, disinfection, and ion-exchange;
- Biological process: pollutants are removed using biological mechanisms, such as aerobic treatment, anaerobic treatment and photosynthetic process (oxidation pond).
Industrial water use accounts for approximately 20% of global freshwater withdrawals. Power generation constitutes a large share of this water usage, with up to 70% of total industrial water used for hydropower, nuclear, and thermal power generation, and 30 to 40% used for other, non-power generation processes.
- Industrial water reuse has the following specific benefits, in addition to the general environmental benefits discussed in earlier sections:
- Potential reduction in production costs from the recovery of raw materials in the wastewater and reduced water usage;
- Heat recovery;
Potential reduction in costs associated with wastewater treatment and discharge. Water reuse and recycling for industrial applications have many potential applications, ranging from simple housekeeping options to advanced technology implementation. Wastewater reuse for industry can be implemented through the reuse of municipal wastewater in industrial processes, internal recycling and cascading use of industrial process water, and non-industrial reuse of industrial plant effluent,
In urban areas, the potential for introducing wastewater reuse is quite high, and reuse options may play a significant role in controlling water consumption and reducing its pollutant load on the environment. A large percentage of water used for urban activities does not need quality as high as that of drinking water. Dual distribution systems (one for drinking water and the other for reclaimed water) have been utilized widely in various countries, especially in highly concentrated cities of the developed countries. This system makes treated wastewater usable for various urban activities as an alternative water source in the area, and contributes to the conservation of limited water resources. In most cases, secondarily treated domestic wastewater followed by sand filtration and disinfection is used for non-potable purposes, such as toilet flushing in business or commercial premises, car washing, garden watering, park or other open space planting, and firefighting.
Applications:
- Reducing environmental impact
- Reducing demands and stress on freshwater supply
- Eliminating the need to transport water
- Improving sustainability
- Avoiding expensive non-compliance fees