Municipal (Sanitary) & Industrial Wastewater Treatment
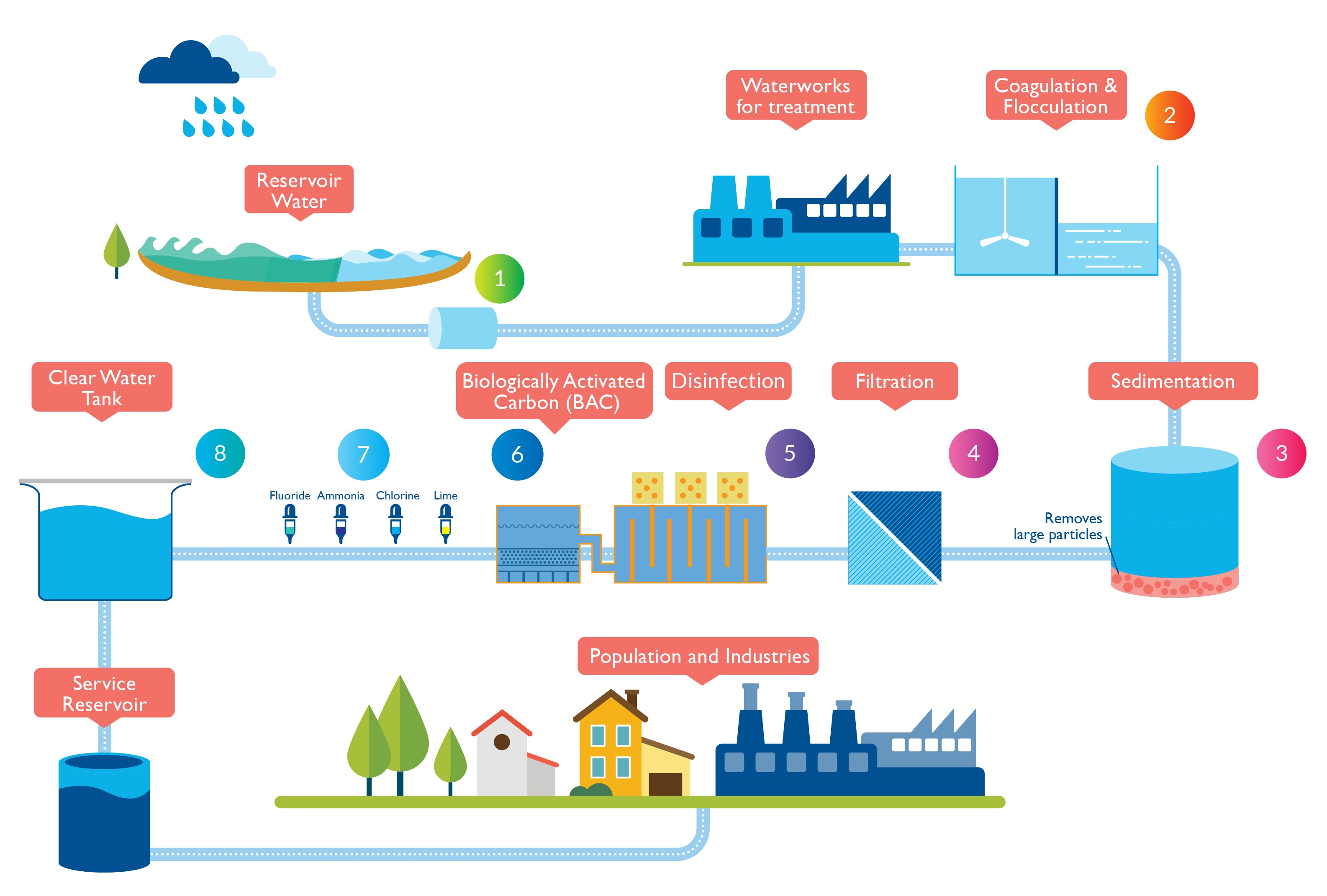
Municipal (Sanitary) Wastewater Treatment is the process of ejecting the harmful pollutants from wastewater. Wastewater collection, transport, and treatment systems are essential to ensure human and environmental well-being. At the urban level, wastewater is returned to the sanitary sewerage system with a contaminant load that must be purified before being discharged into a body of water or used again for other activities.
Municipal wastewater treatment has become one of the most challenging environmental problems due to the volume increase of urban wastewaters and stricter regulations imposed to effluent pollutants concentration. Besides the tough pollutants concentration and flow rate influent disturbances, the influent temperature changes also affect the complex biochemical processes taking place in WWTP bioreactors.
The pollutants are treated by various methods like Physical, Chemical, and Biological process. This treated resource is best for utilizing in raising the crops. The treatment processes in wastewater treatment plants can be divided into different stages of wastewater treatment:
- Physical processes includes the use of screens, filters and sieves, and also settling
- Biological processes such as aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment, biochemical oxidation or sludge digestion
- Chemical processes such as neutralization, disinfection, flocculation and precipitation
The conventional activated sludge (CAS) process has been adopted for handling municipal wastewater, in which soluble organics, ammonium and phosphate are removed mainly via microbial assimilation and dissimilation, including aerobic biological oxidation, nitrification–denitrification, etc. For conventional activated sludge, the sanitary wastewater treatment process are:
- Stage One — Bar Screening.
- Stage Two — Screening.
- Stage Three — Primary Clarifier.
- Stage Four — Aeration.
- Stage Five — Secondary Clarifier.
- Stage Six — Chlorination (Disinfection)
- Stage Seven — Water Analysis & Testing.
- Stage Eight — Effluent Disposal.
Advantages of Conventional Activated Sludge (CAS) are listed as below:
- Low installation cost (Cost effective)
- Good quality effluent
- Small land area requirement
- Loss of head is small
- Freedom from fly and odor nuisance high degree of treatment
- Easily maintained mechanical work
- Self-sustaining system
Aeration can be "conventional rate" based on mechanical aeration, or "extended rate" based on diffused aeration. An extended-aeration system includes capabilities for aeration & mixing, settling, return of activated sludge and solids removal, this last in the form of a biomass known as waste-activated sludge. An activated sludge process re-circulates part of the biomass as an integral part of the process.
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. Industrial facilities may generate the following industrial wastewater flows:
- Manufacturing process wastestreams, which can include conventional pollutants(i.e. controllable with secondary treatment systems), toxic pollutants (e.g. solvents, heavy metals), and other harmful compounds such as nutrients
- Non-process wastestreams: boiler blowdown and cooling water, which produce thermal pollutionand other pollutants
- Industrial site drainage, generated both by manufacturing facilities, service industries and energy and mining sites
- Wastestreams from the energy and mining sectors: acid mine drainage, produced waterfrom oil and gas extraction, radionuclides
- Wastestreams that are by-products of treatment or cooling processes: backwashing (water treatment), brine.
Industrial wastewater could add the following pollutants to receiving water bodies if the wastewater is not treated and managed properly:
- Heavy metals, including mercury, lead, and chromium
- Organic matter and nutrients such as food waste: Certain industries (e.g. food processing, slaughterhousewaste, paper fibers, plant material, etc.) discharge high concentrations of BOD, ammonia nitrogen and oil and grease.
- Inorganicparticles such as sand, grit, metal particles, rubber residues from tires, ceramics, etc.;
- Toxinssuch as pesticides, poisons, herbicides, etc.
- Pharmaceuticals, endocrine disrupting compounds, hormones, perfluorinated compounds, siloxanes, drugs of abuse and other hazardous substances
- Microplasticssuch as polyethylene and polypropylene beads, polyester and polyamide.
- Thermal pollutionfrom power stations and industrial manufacturers
- Radionuclides from uranium mining, processing nuclear fuel, operating nuclear reactors, or disposal of radioactive waste.
- Some industrial discharges include persistent organic pollutantssuch as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
The different types of contamination of wastewater require a variety of strategies to remove the contamination:
- Solids removal
- Oils and grease removal
- Removal of biodegradable organics
- Treatment of other organics
- Treatment of acids and alkalis
- Treatment of toxic materials